Birthplace of Democracy
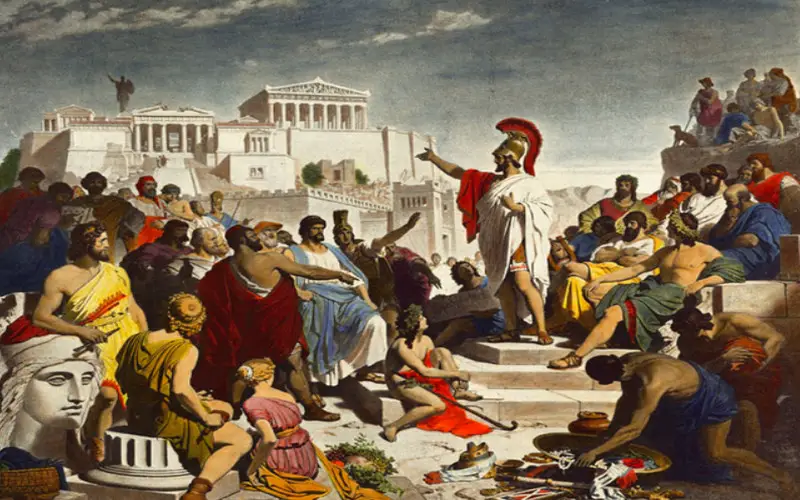

In the 5th century BC, the Athenian statesman Cleisthenes introduced democratic reforms, allowing citizens to participate in decision-making processes. This concept of direct democracy laid the foundation for modern democratic systems and continues to influence political thought and governance worldwide.
The Parthenon

The Parthenon, an iconic temple dedicated to the goddess Athena, is a symbol of Ancient Greece’s architectural and artistic achievements. Constructed in the 5th century BC, this Doric masterpiece represents the epitome of classical Greek architecture. It stands atop the Acropolis in Athens, serving as a testament to the city’s cultural and historical significance.
The Persian Wars
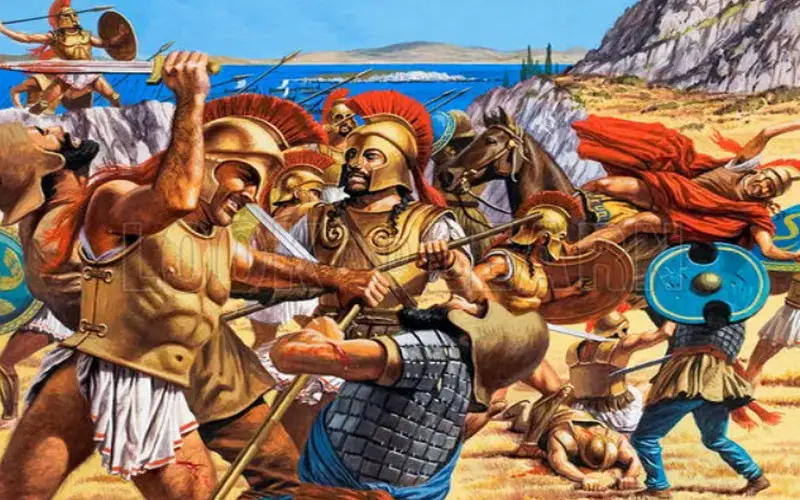

The Persian Wars, a series of conflicts between the Greek city-states and the Persian Empire, were pivotal in shaping Greece’s history. The Battle of Marathon in 490 BC, where the outnumbered Athenians defeated the Persians, and the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC, where King Leonidas and his Spartans valiantly defended against Persian forces, are well-known events from this period.
Alexander the Great
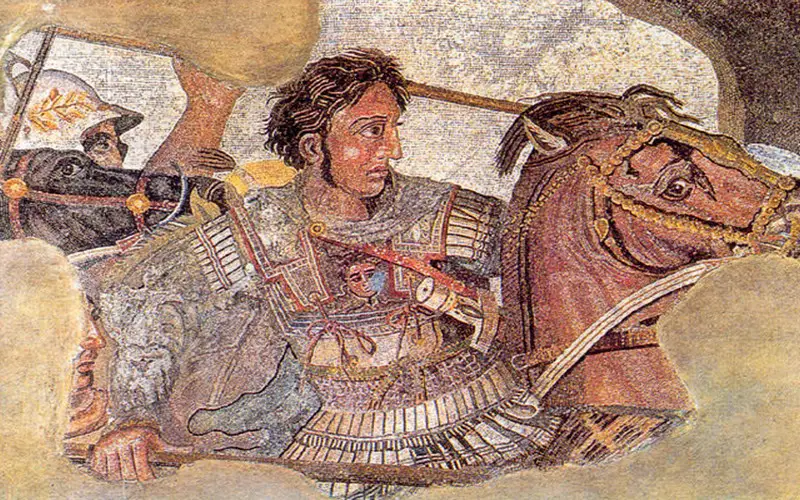

Alexander the Great, born in 356 BC, was one of the most remarkable military tacticians and leaders in history. His conquests extended the Greek Empire across Asia, Europe, and Africa. His reign left an indelible mark on culture, spreading Greek language, art, and ideas throughout his vast empire. This period is known as the Hellenistic era.
The Olympic Games
The Olympic Games, originating in ancient Greece, have a history dating back to 776 BC. These games served as a way to promote physical fitness and foster friendly competition among the Greek city-states.
The Library of Alexandria
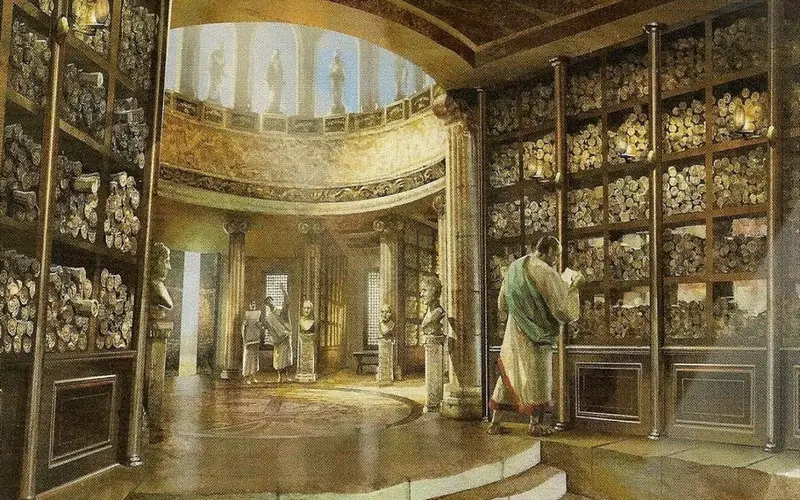

The Library of Alexandria, established by Ptolemy II in the 3rd century BC, was a renowned center of scholarship in the ancient world. It housed countless manuscripts, attracting scholars and thinkers from across the Mediterranean. Unfortunately, this magnificent repository of knowledge was destroyed over time, marking a significant loss for human history.
The Great Philosophers
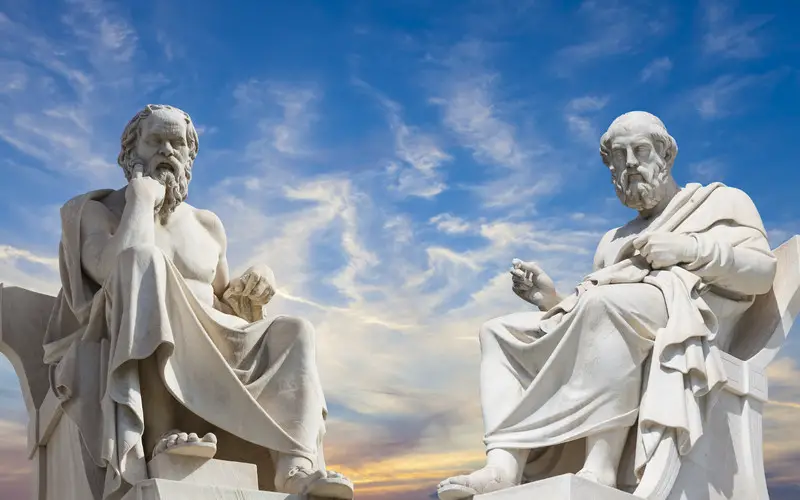

Greece is synonymous with profound philosophical thought, thanks to the contributions of renowned philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. These thinkers laid the groundwork for Western philosophy, exploring topics such as ethics, politics, and the nature of reality. Their enduring ideas continue to influence our understanding of the world.





















