Formation of the Legions
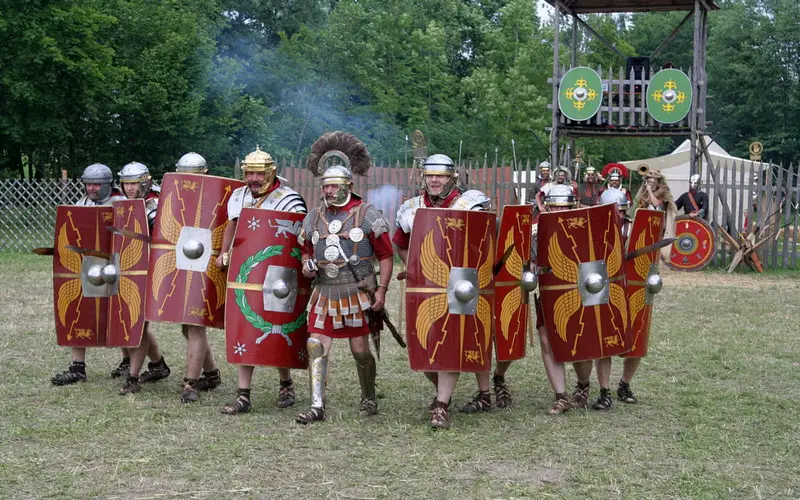

The Roman legions were the backbone of the army, comprised of well-trained and disciplined soldiers known as legionnaires. Each legion consisted of approximately 5,000 infantrymen, supported by cavalry and auxiliary units. These legions were meticulously organized, with soldiers divided into centuries (groups of 100 soldiers) and cohorts (groups of centuries).
Centurions: Leaders of Men
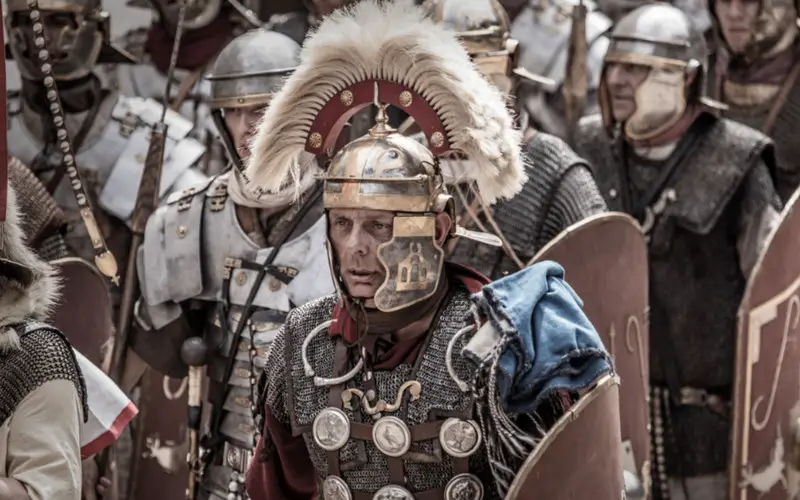

Centurions held significant authority within the Roman military hierarchy. They commanded units of around 80 men known as a century and were responsible for training, discipline, and leading their soldiers into battle. Their leadership was crucial, and their position was earned through merit and battlefield valor.
Rigorous Training and Discipline
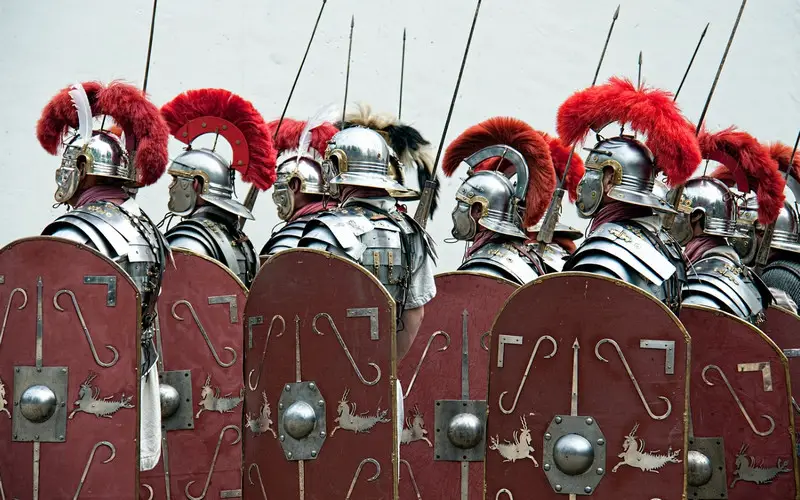

Roman soldiers underwent strict and rigorous training regimes. Discipline was fundamental, and disobedience or desertion was dealt with harshly. Training encompassed marching, weapon proficiency, formation drills, and physical fitness exercises, preparing soldiers for the demanding conditions of battle.
Weaponry and Equipment
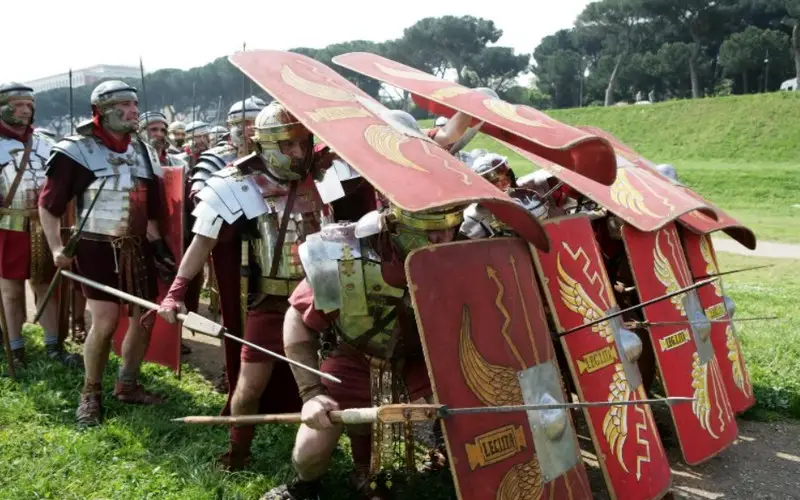

The iconic weapon of the Roman soldier was the gladius, a short sword used for close combat, complemented by a shield called a scutum. Soldiers were also equipped with throwing javelins called pilum, which were effective against enemy formations. Additionally, they wore segmented armor and distinctive helmets, such as the iconic Roman galea.
Engineering and Fortifications
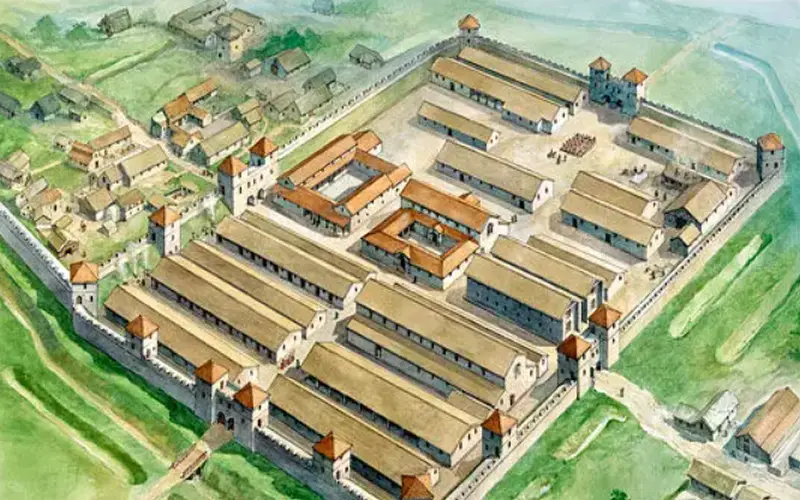
Beyond their combat skills, Roman soldiers were adept at engineering and fortifications. They constructed roads, bridges, and defensive structures such as Hadrian’s Wall in Britain. Their military camps, known as castra, were meticulously planned and fortified, showcasing their engineering expertise.
Mobility and Strategy
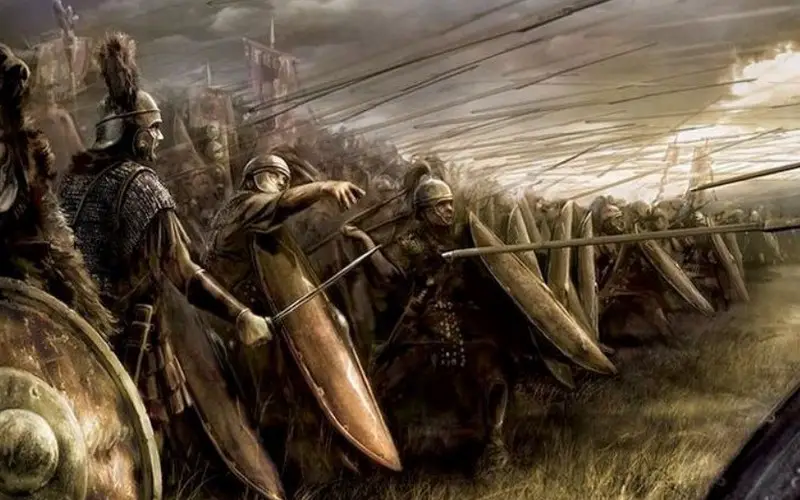

The Roman army was highly mobile, adapting to various terrains and climates during campaigns. They utilized strategic tactics like the “testudo” (tortoise formation), where soldiers formed a shield wall to protect against projectiles, showcasing their adaptability and strategic thinking in battle.
Health and Medical Practices
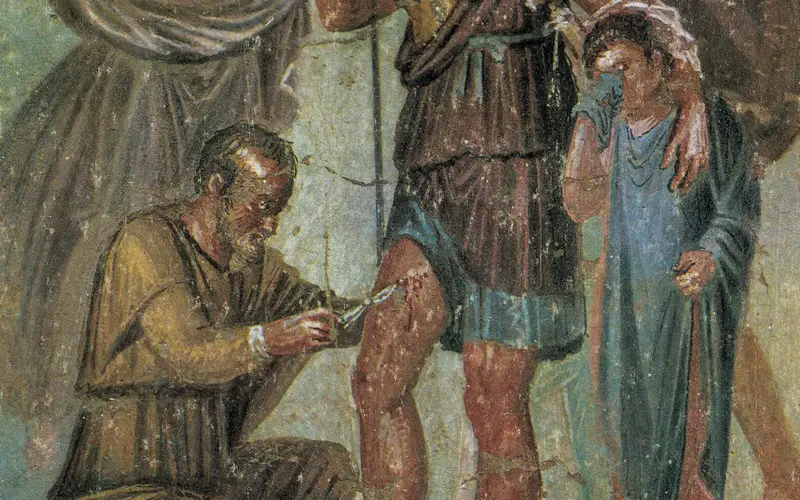

Healthcare for soldiers was a priority in ancient Rome. The army had its hospitals (valetudinaria) with skilled medics and surgeons who treated injuries and illnesses. Innovative medical tools, such as forceps and scalpels, were used for surgeries, indicating advancements in ancient Roman medical practices.




















